Agile project management is an iterative approach to delivering a project. It consists of several iterations or incremental steps to achieve its ultimate goal. Project management in an agile environment is predominantly used in software development projects. It allows you to adjust and refine requirements as you go along rather than following a bottom-up approach. The associated benefits are also realized throughout the process rather than only at the end.
According to an HBR finding 2018, agile adoption has gone beyond IT. As per their survey, about 55% of specific sample organizations have partially implemented agile methodology & processes, and a quarter of the same group has already put it into practice.
The traditional project management method tries to complete the delivery within a stipulated time and budget. It does not allow frequent changes to the business requirements in the middle of the project. Agile project management, on the contrary, fixes time and cost to control the requirements. It heavily relies on the collaboration between the team and the business users to create the right product.
Managing resources is an essential component of project management. They are scarce, expensive, and must be utilized efficiently and effectively. But does resource management play a significant role in the agile development framework? It certainly does, as it is the only way to control project resource costs and complete the delivery satisfactorily.
This article discusses several bottlenecks and their solutions in agile resource planning and management.
What is agile methodology?
Agile methodology is an iterative and incremental approach to project management that involves continuous feedback and adaptation to changing requirements and priorities. It offers a flexible and collaborative approach that helps deliver high-quality products within time and budget.
There are many different agile methods, some of which are Scrum, Kanban, Lean, RAD, and Extreme Programming. Scrum is a robust framework for implementing agile software development processes and other projects. It utilizes short iterations of work, called sprints, and daily meetings, called scrums, to tackle discrete portions of a project until it is completed. Scrum has three key roles: The Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Team members.
The sprint planning meeting is held on the first day of every sprint. After a delivery commitment is made in a sprint planning meeting, the team begins the work and tracks its progress. At the end of each sprint, the stakeholders are invited for a sprint review. The features completed during the sprint are discussed, and feedback is requested.
The product owner keeps track of the feedback and maintains a product backlog with the changes.
In the release-planning meeting, the product owner presents the features they want to be completed in the quarter. Then, the team provides gross-level estimates, which decide the specific features that can be completed in a given sprint. The team also jointly determines how many such features can be completed by the quarter-end.
Release planning can be feature-driven (how many sprints will be required to deliver all the features?), time-driven (how many features can be completed by a specific deadline?), or cost-driven (Important features that must be created within the budget?).
The Scrum methodology requires product backlog (work to be done), sprint backlog, release burndown, and sprint burndown. In addition, the team defines all other forms of documentation as per the specific situation.
The project manager often becomes the scrum master, but this may not always be true. For example, in traditional estimating, all requirements are fully defined, with tasks created and estimated based on their fixed scope. Conversely, agile resource planning and estimation use a top-down method to forecast each sprint.
What are the characteristic traits of agile resource planning?
Agile resource planning is an approach to managing and allocating resources in a flexible and adaptive manner, primarily used in project management and software development contexts. The traits of agile resource planning include:
Flexibility
Agile resource planning emphasizes the ability to quickly respond and adapt to changing project requirements, priorities, and resource needs. It allows for adjustments and reallocation of resources based on evolving circumstances.
Iterative approach
Agile planning is often done in short iterations or sprints, with frequent reassessment and adjustment of resource allocation based on feedback and progress. This iterative nature allows for continuous improvement and optimization of resource utilization.
Collaboration
Agile resource planning encourages collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and resource owners. It involves open communication and close cooperation to ensure that the right resources are available at the right time. Apart from technical and domain knowledge, the following additional skills are also required in an agile resourcing environment. In addition, the following agile characteristics help in delivering high-quality projects.
Prioritization
Agile planning involves prioritizing tasks and resource allocation based on their value and impact. It focuses on delivering high-value features or outcomes early on, enabling stakeholders to provide feedback and make informed decisions.
Continuous monitoring and adaptation
Agile resource planning requires ongoing monitoring of resource usage, progress, and performance. It emphasizes the need to gather data, analyze it, and make necessary adjustments to optimize resource allocation and ensure project success.
These critical traits of agile resource planning help effectively manage resources in dynamic environments. But first, let’s understand the challenges of resource planning in an agile environment.
Challenges of managing resources in agile environment
For projects to be successful, it is vital to have the right resources. While agile methodologies offer flexibility and adaptability, managing resources effectively within this can be complex. Here are some common challenges of managing resources in an agile environment:
Difficulty in managing changing project requirements and scope
Agile projects are characterized by their adaptability and responsiveness to change. However, this flexibility can pose challenges when it comes to resource management. As project requirements evolve, new tasks can emerge, existing tasks can be reprioritized or modified, and additional resources can be added to the project.
If projects managers are unable to anticipate the changes and manage them accordingly, it can lead to last-minute firefighting for resources and overloading of existing employees. This impacts on the project quality and causes delays in delivery.
Inability to manage competing project priorities
Agile projects often operate in dynamic environments where priorities can shift rapidly. Stakeholder requirements, market conditions, or internal organizational changes can lead to changes in project priorities.
Constantly juggling competing priorities and conflicting resource demands can cause significant stress and burnout among team members. It can lead to a decrease in morale and productivity. This, in turn, can further hinder the progress of agile projects.
Conflicting resource demands
In an agile environment, resources typically work on multiple projects concurrently. However, each project has its own set of deadlines, deliverables, and resource requirements which can result in conflicting resource demands and contention among different projects or teams.
This can cause delays, conflicts, and compromises in resource allocation decisions, impacting project progress and overall efficiency. If tasks or projects with high priority are not given the necessary resources, it can result in missed deadlines and compromised project schedules.
Poor communication and collaboration between teams
Effective communication and coordination are crucial for resource management in agile projects. However, lack of proper communication channels, poor resource visibility and dispersed teams can affect the collaboration between team members, stakeholders, and project managers.
This can result in misinterpretations and misalignment of expectations, leading to inefficiencies, duplicated efforts, and rework. As a result, team members may spend more time seeking clarification, impacting the overall productivity and project progress.
This article shows you the importance of collaboration and cross-team collaboration best practices.
Skill gaps and resources shortages
Agile projects often require a diverse range of skills and expertise. However, poor visibility into resources skills, lack of proper training and development opportunities, skill obsolescence, etc., can lead to skill gaps, as team members may not have the necessary competencies to effectively contribute to agile projects.
Without the necessary expertise, teams may make mistakes or overlook critical aspects of the project, leading to failures or low quality of deliverables. In addition, it also affects employee productivity because resources struggle to perform tasks efficiently due to a lack of expertise or resources, resulting in delays in project delivery
Knowing the challenges of resource planning in agile project management, let’s understand how advanced resource management software can help manage resources effectively.
5 best practices for agile resource management
Effective agile resource management helps identify and allocate resources to ensure that teams have the right skills and capacity needed to deliver high-quality results. Here are some best practices for agile resource management:
Leverage cross-functional teams and their skills
Cross-functional teams consist of individuals with a range of expertise and abilities, allowing them to contribute to different aspects of a project. By harnessing this collective knowledge, organizations can optimize resource allocation and utilization for agile projects.
In addition, it promotes flexibility, as team members can adapt to changing project needs and fill gaps in skills or knowledge as required. By leveraging the strengths and capabilities of cross-functional teams, organizations can enhance productivity, deliver high-quality results, and foster a culture of collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Prioritize project tasks based on business value and dependencies
Agile projects typically involve a backlog of tasks, and it is important to prioritize them strategically to maximize the overall project value. By focusing on delivering high-value features or outcomes early in the project, organizations can ensure that the most critical objectives are addressed first.
Additionally, managers need to understand task dependencies to determine the sequence and order in which tasks should be executed. By consistently reassessing and reprioritizing tasks based on their value and dependencies, organizations can ensure that resources are allocated efficiently, resulting in better project outcomes and increased customer satisfaction.
Monitor and track resource utilization
Agile resource management emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring of resource utilization levels throughout the project lifecycle. It involves regularly tracking resource usage, progress, and performance to identify any deviations or issues. By monitoring resource utilization, organizations can identify potential bottlenecks, underutilized resources, or overburdened team members.
This allows project managers to make timely adjustments and reallocate resources as needed. In addition, it helps in being responsive to changes in project requirements, priorities, or constraints and ensures that resources are aligned with the evolving needs of the project, optimizing their utilization and enabling timely delivery of project milestones.
Practice iterative and incremental development
Iterative and incremental development promotes the breaking down of work into smaller units and delivering value incrementally. This enables better estimation, planning, and allocation of resources. By dividing the work into smaller increments, teams can optimize resource utilization, as these units are easier to estimate and allocate.
Additionally, iterative development facilitates prioritization based on feedback, ensuring that teams focus on the most valuable and high-priority items, thus helping in competent allocation. It also allows for adaptability and mitigates risks, as the team can adjust resource allocation in response to changing requirements or emerging opportunities.
Encourage a culture of continuous learning and improvement
To foster a culture of continuous improvement in resource management, it is important to encourage team members to actively pursue learning and growth opportunities. This can be achieved through participation in training programs, workshops, or upskilling activities. By continuously expanding their knowledge and skills, team members can make valuable contributions to the projects.
In addition, embracing a culture of continuous improvement means viewing each iteration or sprint as an opportunity for learning and refining resource management practices. It is crucial to regularly review and adapt processes based on feedback received and the outcomes achieved. This iterative approach enables the team to enhance resource allocation, improve capacity planning, and optimize resource utilization effectively.
These are some of the best practices for efficient resource management in an agile project environment. Now, let’s understand the key features of resource management software to help manage resources in agile projects.
Resource management software for agile framework
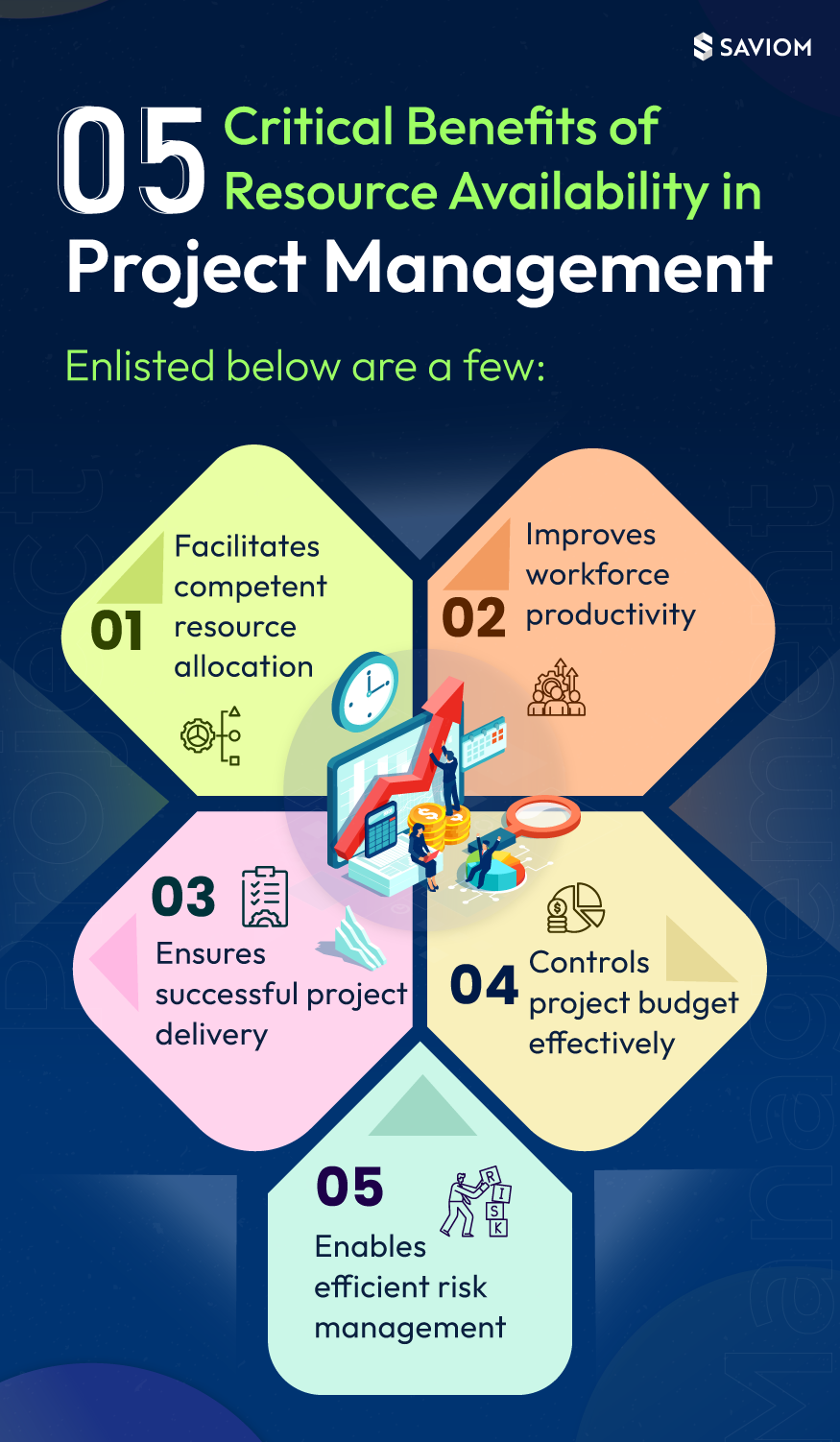
Resource quality plays a significant role in an agile project environment. One cannot optimally use critical resources by assigning work below or above a person’s capability.
One also needs visibility into all the resources – available or not – and their costs. Only then can one balance people, technology, knowledge, time, and budget to deliver on time and goal. This needs to be analyzed before creating WBS (Work Breakdown Structure).
Here are some of the salient features of resource management software to manage agile projects:
Resource or workforce scheduling
Resource scheduling involves identifying and allocating resources for a specific period to different project tasks. With a centralized Gantt chart view of the enterprise, resource scheduling eliminates silos of spreadsheets. It also facilitates deploying the “best-available-best-fit” rather than the “first-available-first-fit” resource. Most agile projects operate with small team sizes. The product backlog will be adversely impacted unless the right resource is deployed for the right task.
Resource utilization
A resource is effective if it works on billable or strategic projects and is fully utilized per its capacity. The efficiency of an organization can be determined by the cumulative utilization of all its employees. Resource managers can proactively mobilize resources from non-billable to billable/ strategic tasks and maximize their billable utilization. Furthermore, ensuring minimum time is spent on mundane tasks such as attending meetings for the scrum team members is crucial.
Forecast shortfall or excesses of resources
Resource capacity is the total number of standard hours an individual is available to work per the employer’s arrangement. Resource demand is understanding the number of resources required to meet the demand for various types of work. Capacity vs. Demand is the process of forecasting shortages or excesses of resources by analyzing the gaps between resources’ capacity against the demand for resources.
It is a shortage of resources when the demand is higher than the capacity or supply of resources. Conversely, it is an excess of resources when the demand is lower than the capacity or supply of resources.
Effective bench management
Bench refers to employees not assigned to any project but on the company’s payroll. They are, in short, kept as reserves by companies on their payroll in anticipation of future projects. If the size of the bench is not controlled, this cost suddenly balloons and significantly affects the company’s bottom line. Therefore, Scrum Master needs to consider bench resource availability during sprint planning.
Forecasted vs. actual use of resource
Resource forecasting predicts various workforce metrics such as demand, supply, vacancies on the bench, resource cost, etc. A resource may be booked for multiple projects where they are expected to spend a certain percentage of the time. Therefore, a timesheet helps record the time an employee spends on each job. This is essential in agile project management to control project costs.
The PMO office verifies if the person concerned has spent the same hours on different activities as per the allocation or if there is a variance.
Managing pipeline projects
The two pipeline management goals are to build a healthy pipeline and win more deals. However, the pipeline or future projects also must be delivered on time and within budget, and one needs advanced resource planning to complete them. Many scheduling software allows creating a project plan using ghost resources, which can be replaced with the existing resources. Since frequent requirement changes are expected within a project that follows agile methodology, timely resource capacity planning is essential.
Supporting matrix structure
In a matrix organizational structure, some individuals report to multiple supervisors or leaders. This relationship can be described as a solid or dotted line of reporting. Managing a shared resource becomes complex when two managers have different project priorities.
It is necessary to ensure that the resource is not overloaded, leading to burnout or unplanned attrition.
Matrix organization can complement the agile project management process when the Scrum Master can access surplus resources in other departments.
Visibility of resource information for decision making
Relevant information about a resource can be viewed using an advanced filter to help decision-making. It can also be made role-specific, e.g., a project manager will only see information related to the projects he manages. On the other hand, a location manager can see resource-related data for the location. These fields could include skillset/competency, cost rate, charge-out rate, etc.
A resource management software with an advanced filtering option can quickly identify appropriate resources for a scrum master.
Forecasting financials
Forecasting is the process of making predictions of the future based on past and present data. To calculate the gross margin for a project, we need to know the charge-out rate and cost to the company of each resource. Most of the projects operate either on a fixed cost or on a time and material basis.
For a fixed-cost project, the revenue amount is already known, and we only need to calculate the resource cost for the project duration.
Scenarios – modelling and simulation
The simulation technique determines how projected performance is affected by changes in the assumptions that those projections are based upon. What-if analysis often compares scenarios and their potential outcomes based on changing conditions. The changes can be simulated in a sandbox environment, and the best possible scenario can be applied to the schedule.
When there is a resource crunch, agile project management can decide on project and resource priorities using simulation.
Business intelligence and reports
Business intelligence provides actionable insights by performing extensive data analysis. Resource management metrics are generated using real-time data, individualized reports, and dashboards. The reports allow managers to make informed decisions and monitor the overall resource health index.
Scrum masters can immensely benefit from the digital dashboards created using real-time business intelligence with changing requirements.
Workforce planning and optimization
Strategic Workforce planning looks at system-wide issues and strategies to:
- Support the organization’s strategic plan (e.g., reorganization and redeployment).
- Address external workforce factors that affect the entire business (e.g., succession planning for retirement bubbles or staff reduction planning for budget cuts).
- Maintain organizational capacity (e.g., in-service training).
- Mitigate risk exposure (e.g., safety planning and Equal Employment Opportunity training).
What is next?
Resources must be utilized efficiently as they are the most high-priced investments of any business. This must be considered while implementing effective resource management in an agile project. In addition, organizations spend a lot of time and cost creating the right talent pool.
Depending on the nature of the project, an appropriate methodology, such as a waterfall or agile, can be adopted. Accordingly, it is necessary to tap the skills and competencies of resources for overall efficiency and profitability.
The Glossary
The SAVIOM Solution
SAVIOM is the market leader in providing Enterprise Resource Management Software. With more than 20 years of experience, SAVIOM’s solution is being used by many Fortune 500 companies across the globe. It also provides tools for project portfolio management, professional service automation, and workforce planning software.
Whether it is Agile, Waterfall, or any other methodology, SAVIOM can provide a comprehensive solution for managing resources.